DBMS Chap 1
We have three levels of abstraction:
Physical level Or Internal Level: This is the lowest level of data abstraction. It describes how data is actually stored in database. You can get the complex data structure details at this level.
End User Don't Know How The Data Is Stored at internal level.
The internal view is described by internal schema.
Internal schema consists of definition of stored record, method of representing the data Field and access method used.
Logical level Or Conceptual Level: This is the middle level of 3-level data abstraction architecture. It describes what data is stored in database And What Is The relationship among those data.
Programmers work at this level .
DBA work at this level
View level Or External Level: Highest level of data abstraction. This level describes the user interaction with database system.
It describes only part of the entire database that a particular end user requires.
End User Can Utilizes Data From This Level .
Example: Let’s say we are storing customer information in a customer table. At physical level these records can be described as blocks of storage (bytes, gigabytes, terabytes etc.) in memory. These details are often hidden from the programmers.
At the logical level these records can be described as fields and attributes along with their data types, their relationship among each other can be logically implemented. The programmers generally work at this level because they are aware of such things about database systems.
At view level, user just interact with system with the help of GUI and enter the details at the screen, they are not aware of how the data is stored and what data is stored; such details are hidden from them.
Explain Mapping. OR
Explain external and internal mapping. OR
What is mapping? Describe type of mapping.
Mapping
The process of transforming requests and results between the three levels is called
mapping.
Types of Mapping
Conceptual/Internal Mapping
External/Conceptual Mapping
Conceptual/Internal Mapping
It relates conceptual schema with internal schema.
It defines correspondence between the conceptual schema and the database stored in
physical devices.
It specifies how conceptual records and fields are presented at the internal level.
If the structure of stored database is changed, then conceptual/internal mapping must be
changed accordingly and conceptual schema can remain invariant.
There could be one mapping between conceptual and internal levels.
External/Conceptual Mapping
It relates each external schema with conceptual schema.
It defines correspondence between a particular external view and conceptual schema.
If the structure of conceptual schema is changed, then external/conceptual mapping must
be changed accordingly and external schema can remain invariant.
There could be several mappings between external and conceptual levels.
Explain Data Independence.
Data Independence
Data independency is the ability to modify a schema definition in one level without
affecting a schema definition in the next higher level.
Types of data independence
Physical data independence
Logical data independence
Physical data independence
Physical data independence allows changing in physical storage devices or organization
of file without change in the conceptual view or external view.
Modifications at the internal level are occasionally necessary to improve performance.
Physical data independence separates conceptual level from the internal level.
It is easy to achieve physical data independence.
Logical data independence
Logical data independence is the ability to modify the conceptual schema without
requiring any change in application programs.
Conceptual schema can be changed without affecting the existing external schema.
Modifications at the logical level are necessary whenever the logical structure of the
database is altered.
Logical data independence separates external level from the conceptual view.
It is difficult to achieve logical data independence.
Types of DBMS Architecture
2. Two tier architecture
3. Three tier architecture
1. Single tier architecture
In this type of architecture, the database is readily available on the client machine, any request made by client doesn’t require a network connection to perform the action on the database.
For example, lets say you want to fetch the records of employee from the database and the database is available on your computer system, so the request to fetch employee details will be done by your computer and the records will be fetched from the database by your computer as well. This type of system is generally referred as local database system.
2. Two tier architecture
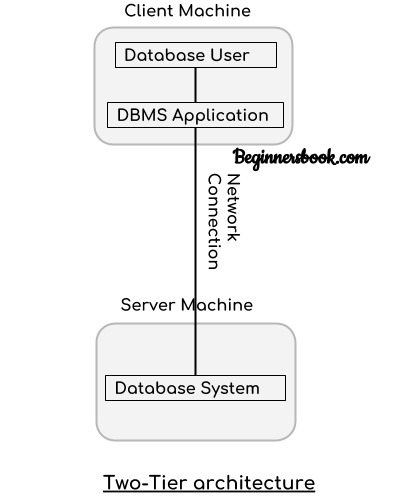
In two-tier architecture, the Database system is present at the server machine and the DBMS application is present at the client machine, these two machines are connected with each other through a reliable network as shown in the above diagram.
Whenever client machine makes a request to access the database present at server using a query language like sql, the server perform the request on the database and returns the result back to the client. The application connection interface such as JDBC, ODBC are used for the interaction between server and client.
3. Three tier architecture
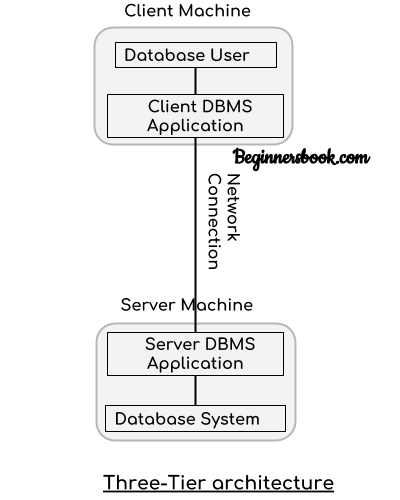
In three-tier architecture, another layer is present between the client machine and server machine. In this architecture, the client application doesn’t communicate directly with the database systems present at the server machine, rather the client application communicates with server application and the server application internally communicates with the database system present at the server.
Explain database system 3 tier architecture with clear diagram ( For Exam)
Most widely used architecture is 3-tier architecture.
3-tier architecture separates it tier from each other on basis of users.
Database (Data) Tier
At this tier, only database resides.
Database along with its query processing languages sits in layer-3 of 3-tier architecture.
It also contains all relations and their constraints.
Application (Middle) Tier
At this tier, the application server and program, which access database, resides.
For a user this application tier works as abstracted view of database.
Users are unaware of any existence of database beyond application.
For database-tier, application tier is the user of it.
Database tier is not aware of any other user beyond application tier.
This tier works as mediator between the two.
User (Presentation) Tier
An end user sits on this tier.
From a user’s aspect, this tier is everything.
He/she doesn't know about any existence or form of database beyond this layer.
At this layer multiple views of database can be provided by the application.
All views which are generated by an application, resides in application tier.
Explain Different Types Of Database Users
1. Naive Users
Naive Users are end users .naive users interacting with database using application program .
They don't have knowledge about database and how data is stored
2. Sophisticated users
They use query language for interact with database . They don't write program . They can creat database applications based on their requirements using Query language.
3. Specialized users
This are sophisticated users who develop complex application programs based on requirements.
4. Application programmers
They are the computer experts . They write code for application . They use different languages like c , developer , coloc etc for writing program code .
5. Database Administrator
Database Administrator defines the schema and also controls the 3 levels of database.
The DBA can create a new account id and password for the user if he/she need to access the data base.
DBA is also responsible for providing security to the data base and he allows only the authorized users to access/modify the data base.
- DBA also monitors the recovery and back up and provide technical support.
- The DBA has a DBA account in the DBMS which called a system or superuser account.
- DBA repairs damage caused due to hardware and/or software failures.
Explain Database System Architecture.
Components of a DBMS
These functional units of a database system can be divided into two parts:
1. Qoury Processor
Storage Manager Units:
Storage manager units provide interface between the low level data stored in database and
the application programs & queries submitted to the system.
1. Authorization Manager — Checks the authority of users to access data.
2 .Integrity Manager — Checks for the satisfaction of the integrity constraints.
3 .Transaction Manager — Preserves atomicity and controls concurrency.
4 .File Manager — Manages allocation of space on disk storage.
5. Buffer Manager — Fetches data from disk storage to memory for being used.
In addition to these functional units, several data structures are required to implement physical
storage system. These are described below:
1. Data Files — To store user data.
2. Data Dictionary — To store metadata.
3. Indices — To provide faster access to data items.
Data Definition language(DDL)
DDL is Data Definition Language and is used to define the structures like schema, database, tables, constraints etc.
It is a set of SQL commands used to create, modify and delete database objects such as
tables, views, indices, etc.
It provides commands like:
CREATE: to create objects in a database.
ALTER: to alter the schema, or logical structure of the database.
DROP: to delete objects from the database.
TRUNCATE: to remove all records from the table
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML is Data Manipulation Language and is used to manipulate data.
It is a set of SQL commands used to insert, modify and delete data in a database.
It provides commands like:
INSERT: to insert data into a table.
UPDATE: to modify existing data in a table.
DELETE: to delete records from a table



Comments
Post a Comment